what is brinell hardness test used for|brinell hardness testing machine diagram : wholesaler Brinell hardness testing is a commonly used method for determining the hardness of metals and alloys. The Brinell hardness test formula. When measuring hardness using the Brinell . Lets try something new with custom jigsaw puzzle for Canada. 1. Use a Family Photo on Puzzle:Make your own puzzle in Canada by choosing a favorite family photo and turn it into a custom puzzle that everyone can enjoy. . Ver mais
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 2 dias atrás · Sistema de Gestão Escolar. Portal do Pai/Aluno, agenda virtual, notas e médias, horários de aula, faltas, ocorrências disciplinares, avisos, informações estudantis.
In this article, we have seen the Brinell hardness test and its two different methods – Standard and Non-Standard Brinell hardness tests. Also, discussed its advantages, disadvantages or limitations, and applications.What is a Brinell Hardness Test? Standards of Brinell Hardness Testing. Brinell Hardness Test Procedure. 1. Preparation of the Specimen. 2. Selection of Load and Indenter. 3. Test .
Brinell hardness testing is a commonly used method for determining the hardness of metals and alloys. The Brinell hardness test formula. When measuring hardness using the Brinell .The Brinell scale / brəˈnɛl / characterizes the indentation hardness of materials through the scale of penetration of an indenter, loaded on a material test-piece. It is one of several definitions of hardness in materials science. History.The Brinell test is frequently used to determine the hardness metal forgings and castings that have large grain structures. The Brinell test provides a measurement over a fairly large area .
Though loads of 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, and 3000 N are available in a typical Brinell hardness tester, a load of 500 N is used for testing relatively soft metals such as copper and aluminium alloys, while the 3000 N load is often used for testing harder materials such as steels and cast irons.However, the general rule is that the combination of test load and ball diameter .Rockwell hardness test is one of the most common indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In contrast to Brinell test, the Rockwell tester measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a .
The Brinell hardness test is not suitable for very hard materials or hardened surface layers because the ball does not penetrate sufficiently into the material. Higher test loads are not the solution at this point, as this leads to .
The Brinell hardness number is designated by the most commonly used test standards (ASTM E10-14[2] and ISO 6506–1:2005) as HBW (H from hardness, B from brinell and W from the material of the indenter, tungsten (wolfram) carbide).The Brinell hardness test. The Brinell hardness test is used for hardness testing larger samples in materials with a coarse or inhomogeneous grain structure. The Brinell hardness test (HBW) indentation leaves a relatively large impression, using a tungsten carbide ball. The size of the indent is read optically.When is the Brinell hardness test used? Brinell hardness testing is a commonly used method for determining the hardness of metals and alloys. The Brinell hardness test formula. When measuring hardness using the Brinell method, a hardened steel or carbide ball of known diameter under a known load is forced into the material being tested.
Common indentation hardness scales are Brinell, Rockwell and Vickers. See also: Hardness. Brinell Hardness Number – Brinell Scale. Brinell hardness test is one of indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In Brinell tests, a hard, spherical indenter is forced under a specific load into the surface of the metal .
The Brinell hardness test is particularly useful for materials with a coarse microstructure or those too rough or thick to be accurately measured using other methods. One of the most popular instruments used for Brinell hardness testing is the King Brinell hardness tester, which is known for its accuracy and reliability.In metallurgy: Testing mechanical properties .oldest of such tests, the Brinell hardness test, uses a 10-millimetre-diameter ball and a 3,000-kilogram load. Brinell hardness values correlate well with UTS.The Brinell hardness number, or simply the Brinell number, is obtained by dividing the load used, in kilograms, by the measured surface area of the indentation, in square millimeters, left on the test surface. The Brinell test is frequently used to determine the hardness metal forgings and castings that have large grain structures. Unlike with Rockwell testing, Brinell tests measure the diameter of the indentation made by the ball, not the depth. A 10mm ball with an applied load of 3,000 kgf is most common for Brinell testing. Brinell tests are ideal for castings and forgings that may have rough surfaces or exhibit some chemical variation.
The Brinell hardness test is used to measure and inspect materials with rough surfaces such as forgings and casting because you cannot use other methods to inspect them. This is because this method uses a large indenter (usually 10 mm) which averages the rough surface of the test piece for better results. It is also used to assess the hardness .
The Brinell hardness number is designated by the most commonly used test standards (ASTM E10-14[2] and ISO 6506–1:2005) as HBW (H from hardness, B from brinell and W from the material of the indenter, tungsten (wolfram) carbide). The Brinell hardness test is used to determine hardness and is done by forcing a hard steel or carbide ball indenter of a specified diameter onto the test metal surface under a specified load. This is followed by measuring the diameter of .Answer: a Explanation: Brinell hardness test uses a hardened steel ball as an indenter. It is 10 mm diameter ball. Diamond indenter is used in the Rockwell test.
When are Brinell hardness tests used? The main drawback of Brinell tests is that they are only valid for relatively soft materials of sufficient thickness. Also, the result is very sensitive to irregularities on the surface of the sample, so it must be clean, flat and polished. Neither can it be spherical or cylindrical.
The typical brinell hardness test uses a 10 millimeters (0.39 in) diameter steel ball as an indenter with a 3,000 kgf (29 kN; 6,600 lbf) force. For softer materials, a smaller force is used; for harder materials, a tungsten carbide ball is substituted for the steel ball. The indentation is measured and hardness calculated as:
The Brinell hardness testing method is used in various cases where large or rough surfaces, coarse-grained materials, or high loads are involved. It is particularly well-suited for testing the hardness of materials with relatively low hardness ranges, such as non-ferrous metals, castings, and softer steels. The Brinell and Rockwell hardness tests are used in nearly every industry. They are critical for understanding what metals and other materials will provide adequate resistance to indentation, abrasion, scratching, and other forms of wear for a given application. Examples include the evaluation of materials for engine pistons, jet turbine blades .The Brinell hardness test is particularly useful for materials with a coarse microstructure or those too rough or thick to be accurately measured using other methods. One of the most popular instruments used for Brinell hardness testing is the King Brinell hardness tester, which is known for its accuracy and reliability.
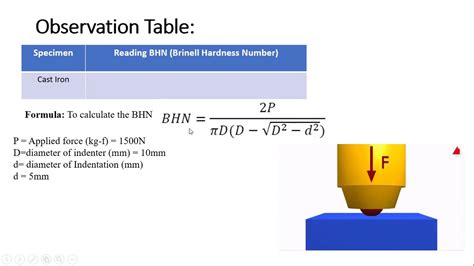
It’s highly versatile and straightforward, making it widely used across industries. Brinell Hardness Test: Using a spherical indenter, this test determines the hardness by measuring the diameter of the indentation created by a known force. It’s suitable for materials with coarse grain structures or rough surfaces.The Brinell hardness test is an empirical indentation hardness test that can provide useful information about metallic materials. This information may correlate to tensile strength, wear resistance, ductility, and other physical characteristics of metallic materials, and may be useful in quality control and selection of materials. .Though loads of 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, and 3000 N are available in a typical Brinell hardness tester, a load of 500 N is used for testing relatively soft metals such as copper and aluminium alloys, while the 3000 N load is often used for testing harder materials such as steels and cast irons.However, the general rule is that the combination of test load and ball diameter .
The Brinell hardness test is named after its inventor, Johan August Brinell. It involves applying a constant load or force to a spherical indenter made of hardened steel or carbide onto the surface of the material being tested. The indentation diameter is then measured optically. The Brinell hardness number (BHN) is calculated as the load .The Brinell method is a static hardness testing method, which can be characterised as follows: It is one of the standardised procedures (ISO 6506, ASTM E10). The Brinell method has a test load range of 1 to 3000 kgf, which means that this method can be used for hardness testing in the low-load and, above all, macro ranges (conventional range).History Behind the Brinell Test. Let’s take a quick glance at the history behind the Brinell test. In 1900, Dr. J.A. Brinell invented this test. As an honor to him, the test named as a Brinell test. It is the oldest hardness test of all time. This test is used to .
how to calculate brinell hardness
When the Brinell hardness test cannot be used, such as when the material’s HB value is greater than 450 or the sample size is too small, the Rockwell hardness test is used instead. This test involves pressing either a diamond cone with a top angle of 120° or a steel ball with a diameter of 1.59 mm or 3.18 mm into the surface of the tested .
lifeproof fre case iphone xs drop test
lifeproof fre drop for s8 plus test
https://m.godzilla777bet.com/?gfs=th4h5phw Plataforma lançamento recarga mínima r$ 20 https://chat.whatsapp.com/K3Jl8dqTrQsDiS7ZV2r0pu Grupinho do WhatsApp de .
what is brinell hardness test used for|brinell hardness testing machine diagram